GCJ2015 还原集合
提交地址找不到 /qd。
假设说我们知道一个数 $x, x > 0$ 我们考虑对其进行背包,不妨假设上一个背包的数组为 $f$。
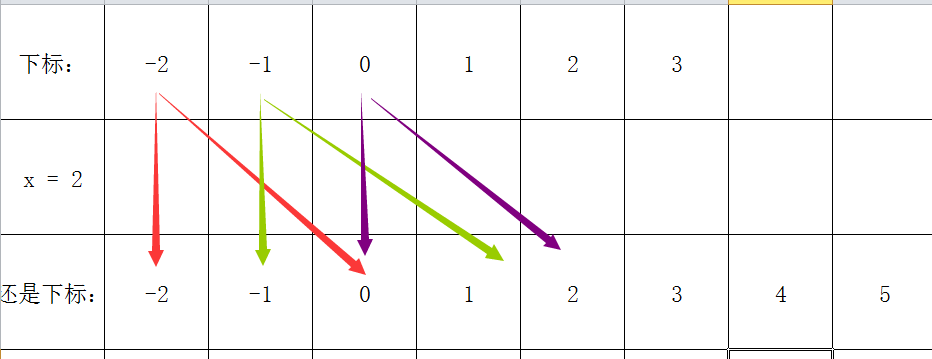
发现对于一个新的数组位置 $i$ 会对应 $i - x, x$ 两个位置。
然后考虑一下 $x, x < 0$ 的情况,位置 $i$ 会对应 $x, i + x$ 两个位置。
发现本质上还原的两个位置只相差了 $x$,所以我们最后还原出来的数列也只是位置相差了 $x$。这个 $x$ 是由若干个数拼接而成的,也就是将一个数取反得到的。
我们考虑如何得到最终答案的一个数,如果当前集合和的最大值减去次大值肯定只有几种情况。
结合一下就是得到的数的绝对值是最小的。我们不妨将所有的数都当做正数来考虑,那么最后得到初始的 $f$ 数组也就是只有 $f_0 = 1$ 。那么我们找那个唯一有值的情况,之后进行背包即可。
如果 $f_0 \ne 1$ 呢?肯定是有若干个 $0$ 组成的集合,也就是 $2^{sum - 1}$,其中 $sum$ 是 $0$ 的数量。
当我们找到这个位置 $f_x = 1$ 而且其他位置都是 $0$ 的时候我们考虑将其他数进行取反。对于背包 $g(i, j)$ 表示考虑第 $i$ 个数,容量为 $j$ 是否被拼成。如果 $g(i, s) = 1$ 而且 $g(i - 1, s - v) = 1$ 那么说明这个数是可以放的。
这里进行背包之后直接进行贪心即可。
背包的空间太大?我们发现最终能够拼成的所有不同权值的集合都已经给出了,我们对于每个权值直接进行离散化即可。
因为一开始我们的 $x$ 肯定是 $< 0$ 的,我们会考虑将其取反,那么我们的权值也需要对应取反一下。
也就是将数轴正负翻转一下即可。
代码实现的话就是直接按照上述过程进行模拟。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#ifdef Fread
char buf[1 << 21], *iS, *iT;
#define gc() (iS == iT ? (iT = (iS = buf) + fread (buf, 1, 1 << 21, stdin), (iS == iT ? EOF : *iS ++)) : *iS ++)
#define getchar gc
#endif
template <typename T>
void r1(T &x) {
x = 0;
char c(getchar());
int f(1);
for(; c < '0' || c > '9'; c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1;
for(; '0' <= c && c <= '9';c = getchar()) x = (x * 10) + (c ^ 48);
x *= f;
}
template <typename T,typename... Args> inline void r1(T& t, Args&... args) {
r1(t); r1(args...);
}
#define int long long
const int maxn = 2e5 + 5;
const int maxm = maxn << 1;
const int inf = 1e15;
void Solve() {
int i, j, n;
r1(n);
struct Node {
int s, p;
int operator < (const Node &z) const {
return s < z.s;
}
};
vector<Node> p(n + 1);
vector<int> v;
for(i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) r1(p[i].s);
for(i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) r1(p[i].p);
sort(p.begin() + 1, p.end());
for(i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) v.push_back(-p[i].s);
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
function<pair<int, int>(void)> gt;
gt = [&] () {
int mx[2]; mx[0] = mx[1] = - inf;
for(i = n; i >= 1; -- i) if(p[i].p) {
if(p[i].s > mx[0]) mx[1] = mx[0], mx[0] = p[i].s;
else mx[1] = max(mx[1], p[i].s);
}
return make_pair(mx[0], mx[1]);
};
int ps0(0);
vector<int> abpos;
while(1) {
pair<int, int> x = gt();
if(x.second == -inf) { ps0 = x.first; break; }
abpos.push_back(x.first - x.second);
int delta = x.first - x.second;
static map<int, int> mp;
mp.clear();
mp[p[1].s] = p[1].p;
for(i = 2; i <= n; ++ i) {
if(mp.count(p[i].s - delta)) p[i].p -= mp[p[i].s - delta];
mp[p[i].s] = p[i].p;
}
}
int T(0);
for(i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) if(p[i].p > 0) { T = log2(p[i].p); break; }
while(T --) abpos.push_back(0);
sort(abpos.begin(), abpos.end());
ps0 = -ps0;
vector<vector<int> > f(abpos.size() + 2, vector<int>(n + 2, 0));
f[0][lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 0) - v.begin()] = 1;
for(i = 0; i < abpos.size(); ++ i) {
f[i + 1] = f[i];
for(j = v.size() - 1; j >= 0 && v[j] - abpos[i] >= 0; -- j) {
int id = lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), v[j] - abpos[i]) - v.begin();
if(v[id] == v[j] - abpos[i])
f[i + 1][j] |= f[i][id];
}
}
for(int i = abpos.size(), ns = lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), ps0) - v.begin(); i > 0; -- i) {
int x = v[ns] - abpos[i - 1];
if(x < 0) continue;
int y = lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x) - v.begin();
if(v[y] == x && f[i - 1][y] == 1) abpos[i - 1] = - abpos[i - 1], ns = y, ps0 += abpos[i - 1];
if(x == 0) break;
}
sort(abpos.begin(), abpos.end());
for(int v : abpos) printf(" %lld", v);
puts("");
}
signed main() {
freopen("recoverset.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("recoverset.out", "w", stdout);
int i, j, T;
r1(T);
for(i = 1; i <= T; ++ i) {
printf("Case #%lld:", i);
Solve();
}
return 0;
}
|







![UOJ 269 [清华集训2016] 如何优雅地求和 题解](https://img.xjh.me/random_img.php?type=bg&ctype=nature&return=302&seed=239604752)

![P4548 [CTSC2006]歌唱王国](https://img.xjh.me/random_img.php?type=bg&ctype=nature&return=302&seed=850658581)
![AT2369 [AGC013C] Ants on a Circle 多解法讨论](https://img.xjh.me/random_img.php?type=bg&ctype=nature&return=302&seed=415064773)
![P7987 [USACO21DEC] Paired Up G 题解](https://img.xjh.me/random_img.php?type=bg&ctype=nature&return=302&seed=199018446)